Latest post
Post Categories
- No categories
Ulcerative Colitis Treatment in Hyderabad
Understanding Ulcerative Colitis: Symptoms, Treatment, and Management
Dive into the complexities of ulcerative colitis, exploring its symptoms, treatment options, and lifestyle management strategies. Gain valuable insights and answers to common questions about this chronic inflammatory bowel disease.
Introduction to Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative colitis is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease that primarily affects the colon and rectum. It is characterized by inflammation and ulcers in the lining of the large intestine, leading to a range of symptoms and complications. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the various aspects of ulcerative colitis, from its symptoms and diagnosis to its treatment options and lifestyle management strategies.
Symptoms and Clinical Presentation
Ulcerative colitis manifests with a variety of symptoms, which can vary in severity and duration. Common symptoms include:
- Abdominal pain and cramping
- Diarrhea, often with blood or mucus
- Rectal bleeding
- Urgency to defecate
- Fatigue and malaise
- Weight loss
- Loss of appetite
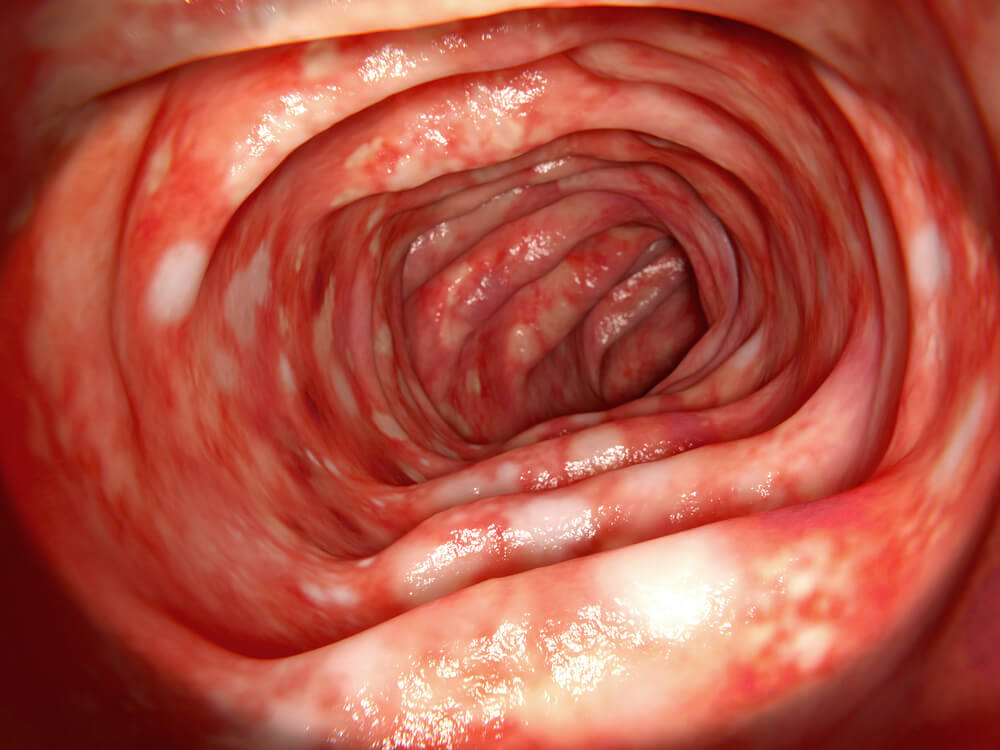
Diagnostic Evaluation
Diagnosing ulcerative colitis involves a combination of clinical evaluation, laboratory tests, and imaging studies. Key diagnostic tests include:
- Colonoscopy with biopsy: To visualize the colon and rectum and obtain tissue samples for analysis.
- Blood tests: To assess for signs of inflammation, anemia, and nutritional deficiencies.
- Stool studies: To rule out infectious causes of colitis.
- Imaging studies: Such as CT scans or MRIs, to evaluate the extent and severity of inflammation.
Medical Treatment Options
The management of ulcerative colitis aims to induce and maintain remission, alleviate symptoms, and prevent complications. Treatment options may include:
- Anti-inflammatory medications: Such as 5-aminosalicylates and corticosteroids, to reduce inflammation in the colon.
- Immunomodulators: Such as azathioprine and methotrexate, to modulate the immune response and maintain remission.
- Biologic therapies: Including TNF-alpha inhibitors and integrin receptor antagonists, to target specific pathways involved in inflammation.
- Topical therapies: Such as rectal suppositories or enemas, to deliver medications directly to the affected area.
Surgical Treatment Options
In cases of severe ulcerative colitis or complications such as toxic megacolon or colorectal cancer, surgical intervention may be necessary. Surgical options may include:
- Colectomy: Surgical removal of the colon and rectum.
- Ileal pouch-anal anastomosis (IPAA): Creation of a pouch from the small intestine to replace the removed colon and rectum, preserving anal continence.
- Proctocolectomy with ileostomy: Surgical creation of an opening in the abdomen (ileostomy) for the elimination of waste.
Lifestyle Management Strategies
In addition to medical and surgical treatments, lifestyle modifications can play a significant role in managing ulcerative colitis and improving quality of life. These may include:
- Dietary modifications: Avoiding trigger foods, maintaining a well-balanced diet, and staying hydrated.
- Stress management: Engaging in relaxation techniques, mindfulness practices, and regular exercise.
- Smoking cessation: Quitting smoking can help reduce the severity of symptoms and decrease the risk of flare-ups.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative colitis is a chronic condition with no known cure, but it can be managed effectively with appropriate medical treatment and lifestyle modifications.
Risk factors for ulcerative colitis include genetic predisposition, environmental factors, immune system dysfunction, and microbial factors.
Ulcerative colitis primarily affects the colon and rectum, while Crohn’s disease can affect any part of the digestive tract, from the mouth to the anus.
Ulcerative colitis may affect fertility in some individuals, but with proper management, most women with ulcerative colitis can have successful pregnancies.
Complications of ulcerative colitis may include severe bleeding, perforation of the colon, toxic megacolon, colorectal cancer, and osteoporosis.
While some individuals may find relief from certain complementary therapies or dietary supplements, it is essential to discuss any alternative treatments with a
healthcare provider to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Conclusion
Ulcerative colitis is a complex and challenging condition that requires ongoing management and support. By understanding the symptoms, treatment options, and lifestyle management strategies discussed in this article, individuals with ulcerative colitis can take proactive steps to manage their condition effectively and improve their overall quality of life.
