Latest post
Post Categories
- No categories
Acute Appendicitis Treatment in Hyderabad
Understanding Acute Appendicitis: A Comprehensive Guide
Explore the complexities of acute appendicitis, a common surgical concern. Learn about its incidence, treatment options, and emerging research on nonoperative management. Gain insights into the pathophysiology, diagnostic implications, and treatment strategies.
Introduction
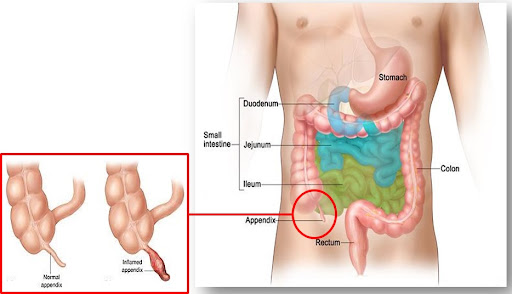
Acute appendicitis is a prevalent concern encountered by general surgeons, constituting approximately 1% of all surgical operations. In the United States, the
annual incidence is estimated at 9.38 per 10,000, showing a slight increase over the past two decades. While the conventional approach involves appendectomy, recent research explores nonoperative management’s safety and efficacy. This chapter delves into the pathophysiology, diagnostic implications, and treatment strategies for patients with appendicitis and appendiceal neoplasm.
The Most Commonly Accepted Treatment
Appendectomy: A Surgical Staple:
- Unveiling the primary course of treatment for acute appendicitis.
- Insight into the significance of appendectomy.
- Statistical overview: Approximately 300,000 appendectomies annually in the United States
Emerging Paradigms: Nonoperative Management
Shifting Perspectives:
- Investigating the increasing research on nonoperative management.
- Safety and efficacy considerations.
- Patient selection criteria for nonoperative approaches.
Diagnostic Challenges and Implications
Navigating the Diagnostic Landscape:
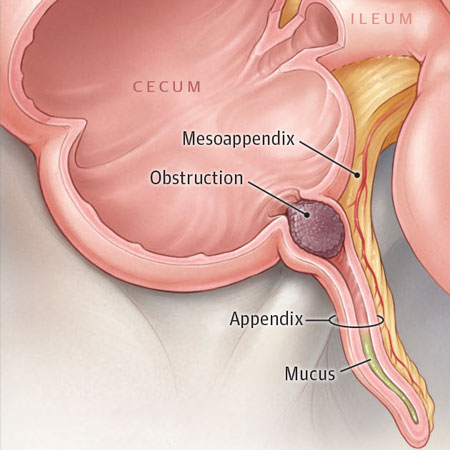
- Challenges in diagnosing appendicitis.
- Role of imaging studies, laboratory tests, and clinical evaluation.
- Implications of accurate and timely diagnosis.
Treatment Strategies
Comprehensive Approaches:
- Tailoring treatment strategies based on patient factors.
- Overview of surgical and nonoperative options.
- Collaborative decision-making between patients and healthcare providers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Acute Appendicitis
While some cases may resolve with antibiotics, surgical intervention remains the most accepted and effective treatment.
Nonoperative management is being explored as an alternative, particularly in uncomplicated cases. However, it requires careful consideration.
Untreated appendicitis can lead to complications such as perforation, abscess formation, and peritonitis, emphasizing the importance of timely intervention.
No specific dietary measures are proven to prevent appendicitis. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is generally advisable.
While imaging studies play a crucial role, clinical evaluation and laboratory tests are also essential for an accurate diagnosis.
Laparoscopic appendectomy is a minimally invasive surgical technique associated with faster recovery and fewer complications compared to traditional open surgery.
Conclusion
This comprehensive guide provides valuable insights into acute appendicitis, addressing its incidence, treatment options, and the evolving landscape of nonoperative management. By understanding the pathophysiology, diagnostic challenges, and treatment strategies, both healthcare providers and patients can make informed decisions, emphasizing the importance of a collaborative approach in managing this common surgical concern.
