Latest post
Post Categories
- No categories
Colonic Bleeding and Ischemia Treatment in Hyderabad
Colonic Bleeding: A Common Yet Serious Concern
Discover why colonic bleeding is common, its various causes, and how it’s diagnosed and treated. Learn about the significance of conservative management and surgical intervention in addressing this condition.
Introduction
Colonic bleeding is a prevalent issue affecting adults, leading to hospitalization and even mortality in severe cases. Understanding its etiologies, diagnostic approaches, and treatment modalities is crucial for effective management. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of colonic bleeding, exploring its diverse causes, diagnostic methods, and treatment options.
Colonic bleeding is common, affecting a significant portion of the adult population. This condition poses various challenges, including the risk of hospitalization and mortality. Understanding its prevalence and underlying causes is essential for early detection and intervention.
Etiologies of Colonic Bleeding
Colonic bleeding can stem from multiple etiologies, ranging from benign to more severe conditions. Understanding these underlying causes is vital for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Let’s explore some common etiologies of colonic bleeding:
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
- Diverticular Disease
- Colonic Polyps
- Colorectal Cancer
- Vascular Malformations
Each of these etiologies presents unique challenges in diagnosis and management, highlighting the importance of a comprehensive approach to colonic bleeding.
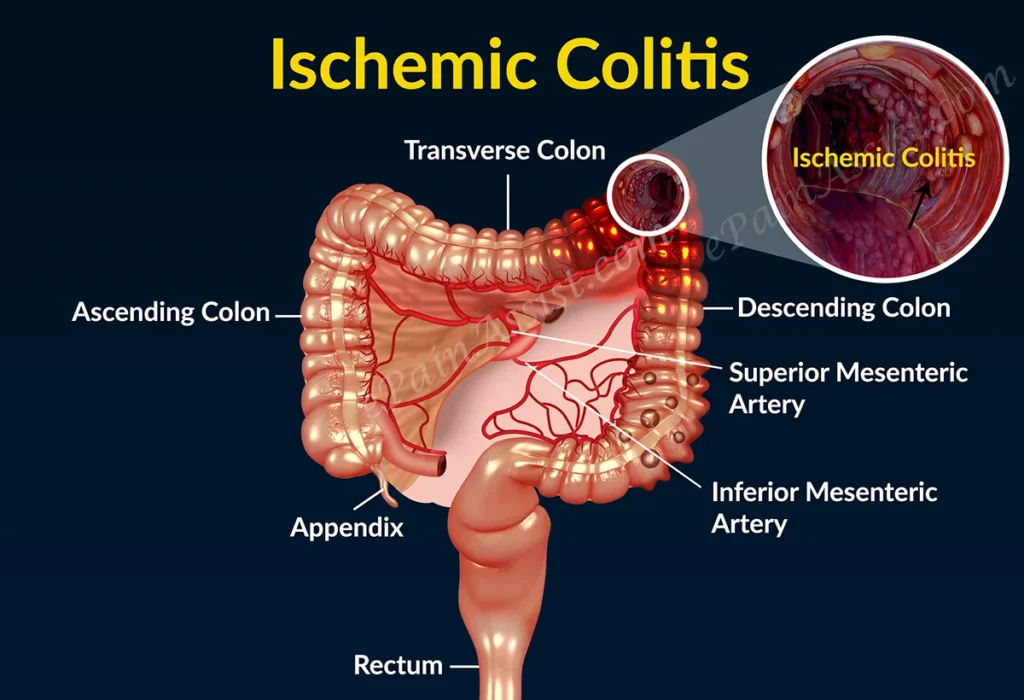
Small Intestinal Intussusception
Small intestinal intussusception involves the small intestine and is often seen in infants and young children. It can lead to severe abdominal pain, vomiting, and bloody stools.
Colonic Intussusception
Colonic intussusception affects the colon and is more common in adults. It is often associated with underlying conditions such as colonic tumors.
Diagnosing Intussusception
Computed tomography (CT) is the most accurate diagnostic modality for intussusception. It helps identify the presence of intussusception and any underlying causes such as gastrointestinal malignancies.
Treating Intussusception
In adults, intussusception is often associated with a gastrointestinal malignancy in up to 56% of cases. The primary treatment is resection without reduction, which involves surgical removal of the affected segment of the intestine.
Understanding Colonic Volvulus
Colonic volvulus occurs when a segment of the colon undergoes torsion along its own mesentery, resulting in obstruction. It is a rare condition in the Western world but more common in regions like Africa, the Middle East, and South America.
Sigmoid Volvulus
Sigmoid volvulus is the most common form of colonic volvulus. It occurs when the sigmoid colon becomes twisted along a chronically elongated mesentery.
Diagnosing Colonic Volvulus
Plain radiography can be diagnostic for sigmoid volvulus, but characteristic findings can also be seen on barium enema and CT scans. Endoscopy is successful in decompressing sigmoid volvulus in many cases.
Treating Colonic Volvulus
The treatment of colonic volvulus depends on the specific subtype. For sigmoid volvulus, endoscopic decompression is often attempted initially, followed by surgical resection if necessary.
Diagnosis of Colonic Bleeding
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective management of colonic bleeding. Various diagnostic techniques are employed to identify the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Let’s explore some key diagnostic methods:
- Colonoscopy
- CT Angiography
- Capsule Endoscopy
- Radionuclide Scanning
These diagnostic modalities enable healthcare providers to assess the extent of bleeding and determine the most appropriate course of treatment.
Treatment Approaches
The treatment of colonic bleeding varies depending on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. From conservative management to surgical intervention, various approaches are employed to address this challenging condition. Let’s explore some treatment options:
- Conservative Management
- Endoscopic Therapy
- Transarterial Embolization
- Surgical Resection
Each treatment approach has its indications and considerations, highlighting the importance of individualized care for patients with colonic bleeding.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Common symptoms include rectal bleeding, changes in bowel habits, abdominal pain, and fatigue.
While colonic bleeding can indicate serious conditions such as colorectal cancer, it can also stem from benign causes like hemorrhoids.
Diagnostic methods include colonoscopy, CT angiography, capsule endoscopy, and radionuclide scanning.
The prognosis varies depending on the underlying cause and severity of the bleeding. Early detection and intervention improve outcomes.
While some causes of colonic bleeding may not be preventable, maintaining a healthy lifestyle and regular screenings can reduce the risk.
It’s essential to seek medical attention promptly. Your healthcare provider can perform the necessary tests to determine the cause of your symptoms and
recommend appropriate treatment.
Conclusion
Colonic bleeding is a complex condition with multiple etiologies, diagnostic challenges, and treatment considerations. By understanding the underlying causes, diagnostic methods, and treatment options, healthcare providers can effectively manage this condition and improve patient outcomes.
