Latest post
Post Categories
- No categories
Crohns Treatment in Hyderabad
Exploring Crohn's Disease: Symptoms, Treatment, and Lifestyle Management
Discover comprehensive insights into Crohn’s disease, including its symptoms, treatment options, and lifestyle management strategies. Get expert guidance and answers to common questions about this chronic inflammatory condition.
Introduction to Crohn’s Disease
Crohn’s disease is a chronic inflammatory condition that primarily affects the gastrointestinal tract. It is characterized by inflammation and damage to the lining of the digestive system, leading to a range of symptoms and complications. In this article, we will delve into the various aspects of Crohn’s disease, including its symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and lifestyle management strategies.
Understanding Crohn’s Disease
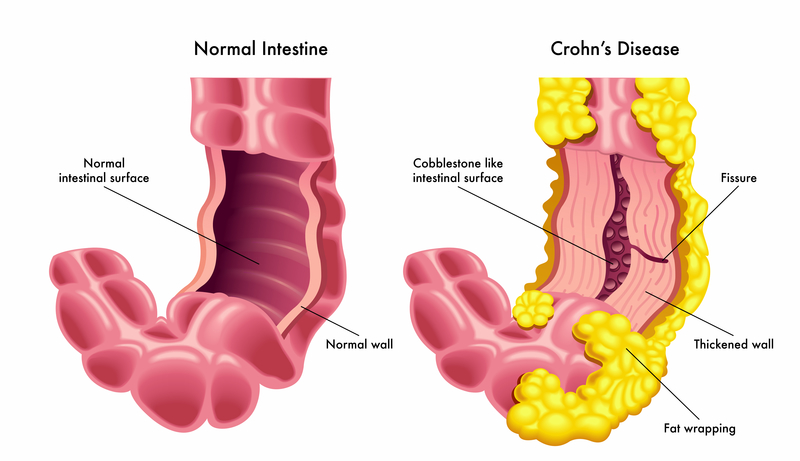
Crohn’s disease is a complex condition with diverse manifestations that can vary widely among individuals. It can affect any part of the digestive tract, from the mouth to the anus, and is often associated with periods of flare-ups and remission. Common symptoms of Crohn’s disease include abdominal pain, diarrhea, rectal bleeding, weight loss, and fatigue.
Diagnostic Evaluation
Diagnosing Crohn’s disease involves a combination of clinical evaluation, laboratory tests, imaging studies, and endoscopic procedures. These may include blood tests, stool studies, imaging tests such as CT scans or MRIs, and endoscopic procedures like colonoscopy or upper endoscopy. A comprehensive diagnostic approach is essential for accurate diagnosis and appropriate management.
Medical Treatment Options
The management of Crohn’s disease typically involves a combination of medical therapies aimed at controlling inflammation, relieving symptoms, and preventing complications. Commonly used medications for Crohn’s disease include:
- Anti-inflammatory Drugs: Such as corticosteroids, mesalamine, and immunomodulators.
- Biologic Therapies: Including TNF-alpha inhibitors, interleukin inhibitors, and integrin receptor antagonists.
- Antibiotics: To treat infections and reduce inflammation in the gut.
Surgical Treatment Options
In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary for complications of Crohn’s disease or when medical therapy is ineffective. Surgical options for Crohn’s disease may include:
- Strictureplasty: Surgical widening of narrowed segments of the intestine.
- Bowel Resection: Removal of diseased portions of the intestine.
- Fistula Repair: Closure of abnormal connections between the intestine and other organs. Ileostomy or Colostomy: Surgical creation of an opening in the abdomen for the elimination of waste.
Lifestyle Management Strategies
In addition to medical and surgical treatments, lifestyle modifications can play a crucial role in managing Crohn’s disease and improving quality of life. These may include:
- Dietary Modifications: Avoiding trigger foods, maintaining a balanced diet, and staying hydrated.
- Stress Management: Engaging in relaxation techniques, exercise, and activities that promote mental well-being.
- Smoking Cessation: Quitting smoking can help reduce the severity of symptoms and decrease the risk of complications.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Crohn's Disease
The exact cause of Crohn’s disease is unknown, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic, environmental, and immune factors.
Individuals with Crohn’s disease may need to avoid certain foods that can trigger symptoms, such as high-fiber foods, dairy products, spicy foods, and alcohol.
Crohn’s disease is a chronic condition with no cure, but it can be managed effectively with medications, lifestyle modifications, and sometimes surgery.
Long-term complications of Crohn’s disease may include bowel obstructions, fistulas, abscesses, malnutrition, osteoporosis, and an increased risk of colorectal cancer.
Pregnancy can influence the course of Crohn’s disease, but with proper management and monitoring, most women with Crohn’s disease can have successful pregnancies.
There is a genetic component to Crohn’s disease, and individuals with a family history of the condition may have an increased risk of developing it themselves
Conclusion
Crohn’s disease is a chronic inflammatory condition that requires ongoing management and support. By understanding the symptoms, treatment options, and lifestyle management strategies discussed in this article, individuals with Crohn’s disease can take proactive steps to manage their condition effectively and improve their overall quality of life.
