Latest post
Post Categories
- No categories
Rectovaginal and Rectourethral Fistulas Treatment in Hyderabad
Call: +91-7013714402
Addressing the Challenges of Genitourinary and Digestive Tract Fistulas
Learn about the diagnosis, classification, work-up, and management of rectovaginal and rectourethral fistulas, which pose significant challenges despite not often being life-threatening.
Introduction
Fistulas between the genitourinary and digestive tracts present complex challenges for patients and healthcare providers alike. While not typically life-threatening, these fistulas profoundly impact patients’ quality of life. This comprehensive guide explores the diagnosis, classification, work-up, and management of rectovaginal and rectourethral fistulas, shedding light on effective treatment approaches.
Understanding Genitourinary and Digestive Tract Fistulas
Fistulas between the genitourinary and digestive tracts, including rectovaginal and rectourethral fistulas, represent intricate medical conditions requiring specialized care and management.
Impact on Quality of Life
Despite not being life-limiting, these fistulas significantly impair patients’ daily functioning, leading to emotional distress and physical discomfort.
Diagnostic Challenges
Diagnosing genitourinary and digestive tract fistulas is often straightforward, yet their management poses substantial challenges due to various factors.
Causes and Classification
Understanding the underlying causes and classifying fistulas is crucial for devising appropriate treatment strategies and optimizing patient outcomes.
Radiated Tissue Damage
Fistulas often develop as a complication of radiation therapy, leading to tissue damage and fistula formation.
Septic Complications
Infection-related complications further complicate the management of genitourinary and digestive tract fistulas, requiring prompt intervention to prevent systemic complications.
Work-up and Evaluation
A comprehensive work-up is essential for accurately diagnosing and characterizing genitourinary and digestive tract fistulas, guiding subsequent management decisions.
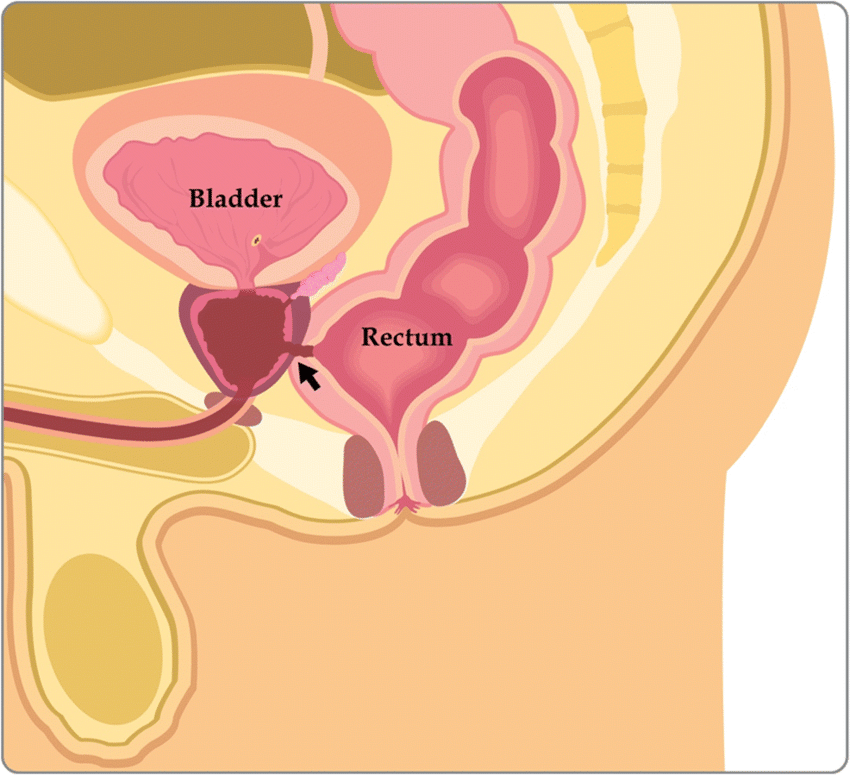
Diagnostic Imaging
Advanced imaging modalities, such as MRI or CT scans, are invaluable for visualizing fistulas and assessing their extent.
Endoscopic Evaluation
Endoscopic procedures, including cystoscopy and sigmoidoscopy, play a vital role in directly visualizing fistulas and guiding treatment planning.
Management Strategies
Managing genitourinary and digestive tract fistulas requires a multidisciplinary approach and personalized treatment strategies tailored to each patient’s unique needs.
Surgical Interventions
Surgical repair of fistulas may be necessary, involving meticulous dissection and closure techniques to restore normal anatomy and function.
Medical Therapies
Adjunctive medical therapies, including antibiotics or immunosuppressive agents, may be prescribed to address underlying infection or inflammation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Common symptoms include fecal or urinary incontinence, vaginal discharge, pelvic pain, and recurrent urinary tract infections
While some fistulas may spontaneously close, most require surgical intervention or medical management to promote healing and prevent complications.
Nonsurgical options such as wound care, dietary modifications, and medication management may be considered for select patients, particularly those with lowoutput fistulas.
Recovery time varies depending on the type and complexity of the fistula repair, ranging from a few weeks to several months for complete healing and restoration of function.
While surgical repair aims to achieve complete closure of the fistula, recurrence can occur, necessitating additional interventions or therapies.
Yes, regular follow-up appointments with healthcare providers specializing in pelvic floor disorders are essential to monitor healing progress and address any
complications
Conclusion
Genitourinary and digestive tract fistulas represent challenging conditions that significantly impact patients’ quality of life. By understanding their diagnosis, classification, and management, healthcare providers can effectively address these complex issues and improve patient outcomes.
Contact Us
Book An Appointment!
To schedule a consultation with our expert colorectal surgery team or inquire about
our services, please contact us at:
Address
212, Kokapet Terminal, Gandipet Main Rd, Kokapet, Hyderabad, Telangana 500075
Phone
+91-7013714402
info@colorectalclinic.com
