Latest post
Post Categories
- No categories
Sacrococcygeal Pilonidal Disease and Perianal Hidradenitis Suppurativa Treatment in Hyderabad
Understanding Sacrococcygeal Pilonidal Disease (PD)
Navigating Sacrococcygeal Pilonidal Disease and Perianal Hidradenitis Suppurativa: Understanding, Treatment, and Management.
Explore the complexities of Sacrococcygeal pilonidal disease (PD) and Perianal hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), understanding their etiology, treatment options, and management strategies for optimal patient care.
Introduction
This article delves into the intricacies of Sacrococcygeal pilonidal disease (PD) and Perianal hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), shedding light on their underlying causes, treatment modalities, and management challenges.
Understanding the etiology and clinical presentation of Sacrococcygeal pilonidal disease (PD) is crucial for devising effective treatment strategies and minimizing the risk of recurrence.
Etiology and Incidence
PD is an acquired disease resulting from subcutaneous trauma of hair shafts, with an estimated incidence of 26 per 100,000 people. Young adults are particularly affected, facing significant morbidity due to the chronicity of the disease.
Clinical Presentation
PD often presents with symptoms such as pain, swelling, and recurrent abscess formation in the sacrococcygeal region, leading to significant discomfort and impaired quality of life.
Treatment Modalities for PD
Effective management of PD requires a multimodal approach encompassing both conservative and surgical interventions tailored to the severity of the disease and individual patient factors.
Conservative Management
Conservative management options for PD include simple incision and drainage of abscesses, along with measures to promote wound healing and prevent recurrence.
Surgical Interventions
Surgical options for PD range from excision with flap reconstruction to minimize wound complications and recurrence, despite the challenges associated with extensive surgical interventions.
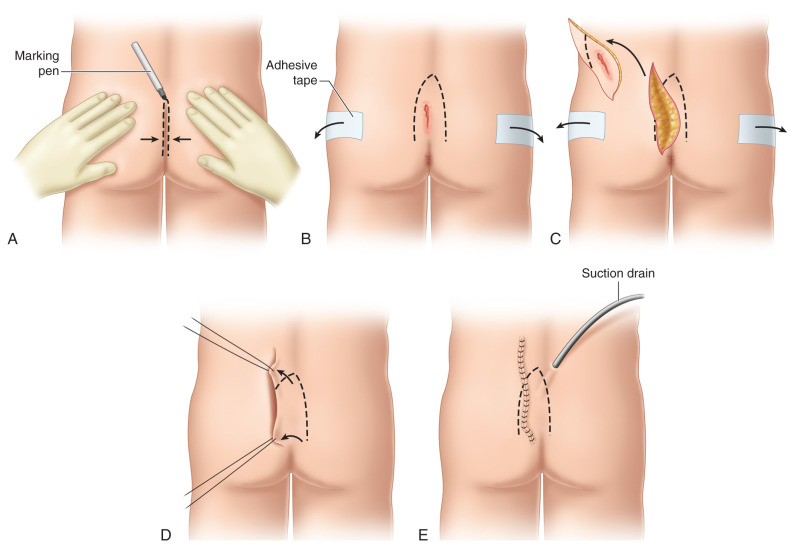
Managing Perianal Hidradenitis Suppurativa (HS)
Perianal hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) poses significant challenges in terms of diagnosis, management, and optimizing patient outcomes.
Etiology and Pathogenesis
HS is an acquired condition resulting from recurrent inflammation of the apocrine glands in the perianal skin, leading to abscess formation and chronically draining sinuses.
Medical Therapy
Medical therapy plays a crucial role in managing HS, particularly in mild disease, where it serves as a useful adjunct for symptom control and preventing disease progression.
Surgical Approaches
Surgical management of HS involves a variety of approaches, including incision and drainage of acute abscesses, along with more extensive procedures such as unroofing of sinus tracts and wide excision with or without grafting for chronic disease.
Comparative Analysis and Challenges
Comparing the treatment strategies for PD and HS highlights the complexities of managing chronic inflammatory conditions in the perianal region, emphasizing the need for individualized treatment plans and multidisciplinary care.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Common symptoms include pain, swelling, and recurrent abscess formation in the sacrococcygeal region.
No, conservative management options such as simple incision and drainage are available for mild cases of PD.
A multimodal approach combining medical therapy and surgical interventions is recommended for managing HS, tailored to the severity of the disease and individual patient factors.
While surgery can provide symptomatic relief and improve quality of life, HS is a chronic condition that may require ongoing management and monitoring.
Complications may include wound infections, delayed wound healing, and recurrence of disease, highlighting the importance of careful patient selection and surgical technique.
Conclusion
This comprehensive overview highlights the complexities of Sacrococcygeal pilonidal disease (PD) and Perianal hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), emphasizing the need for a multidisciplinary approach to optimize patient care and outcomes.
Contact Us
Book An Appointment!
To schedule a consultation with our expert colorectal surgery team or inquire about
our services, please contact us at:
Address
212, Kokapet Terminal, Gandipet Main Rd, Kokapet, Hyderabad, Telangana 500075
Phone
+91-7013714402
info@colorectalclinic.com
